|
您目前处于:Development
2013-06-22
|
|
1. 堆Heap 定义 堆是一颗安全二叉树,其结点含有Comparable的对象。在最大堆中,每个结点的对象都大于等于它的子孙结点中的对象。 public interface MaxHeapInterface<T extends Comparable<? super T>> {
public void add(T newEntry);
public T removeMax();
public T getMax();
public boolean isEmpty();
public int getSize();
public void clear();
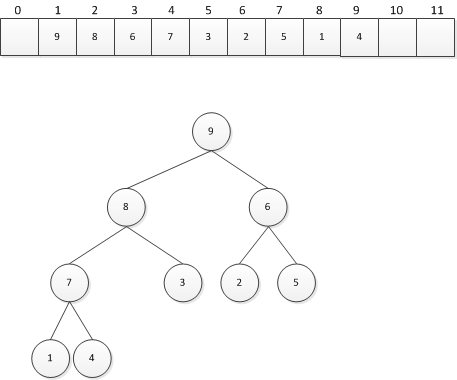
}2. 用数组表示堆 用数组表示完全二叉树:一个完全二叉树在其倒数第二层以上是满的,并且其最后一层上的叶子结点是从左到右填满的。因此,指导最后一片叶子,完全二叉树中没有空洞。 如果一颗二叉树是完全的,使用数组而不是链表会更好。可以使用层序遍历将这棵二叉树的数据存放到一个数组中的连续位置。这种表示可以容易地找到一个结点的双亲或孩子中的数据。如果从数组的索引1开始存放二叉树,即跳过数组的第一个位置,则数组索引i处结点的: 双亲在索引i/2处,除非该结点是根节点(i为1); 子结点在索引2i与2i+1处。
MaxHeap类 public class MaxHeap<T extends Comparable<? super T>> implements
MaxHeapInterface<T>, Serializable {
private T[] heap; // 存放堆元素的数组
private int lastIndex; // 最后一个元素的索引
private static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 25;
public MaxHeap() {
this(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY);
}
public MaxHeap(int initialCapacity) {
heap = (T[]) new Comparable[initialCapacity + 1];
lastIndex = 0;
}
// 插入元素
public void add(T newEntry) {
// 代码如下
}
public T removeMax() {
// 代码如下
}
public T getMax() {
T root = null;
if (isEmpty())
root = heap[1];
return root;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return lastIndex < 1;
}
public int getSize() {
return lastIndex;
}
public void clear() {
for (; lastIndex > -1; lastIndex--)
heap[lastIndex] = null;
lastIndex = 0;
}
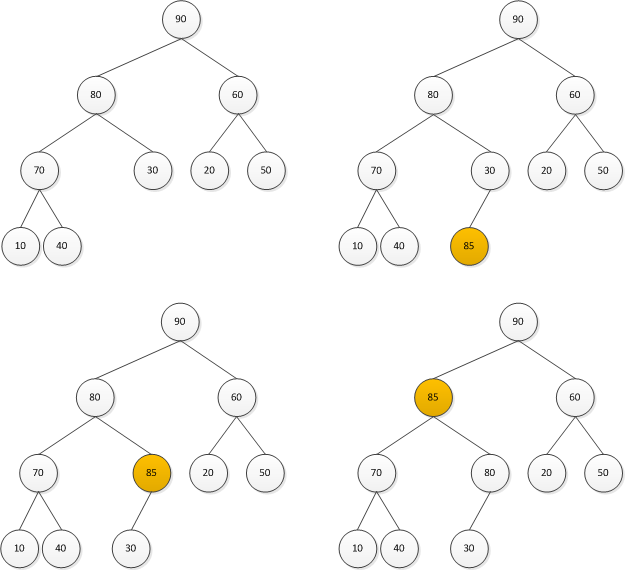
}3. 堆:插入元素 交换算法
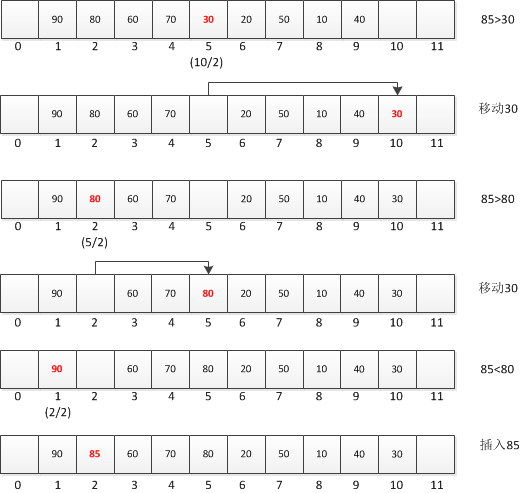
避免交换 在数组索引10处有可用于新元素的空间,这个位置的双亲是位置10/2,即5,因而将新元素85与索引5处的内容30比较,由于85>30,所以将30移动到索引10处。 这时,在数组索引5处有可用于新元素的空间,这个位置的双亲是位置5/2,即2,则将新元素85与索引2处的内容80比较,由于85>80,所以讲80移动到索引5处。 这时,在数组索引2处有可用于新元素的空间,这个位置的双亲是位置2/2,即1,则将新元素85与索引1处的内容90比较,由于85<90,所以讲85插入索引2处。
为了将新元素插入堆,要从下一个可用于叶子的空闲位置开始。跟踪从该叶子到根的路径,直到找到新元素的正确位置。在这样做的同时,将元素从双亲向子结点移动以便最终为新元素腾出空间。 插入代码 public void add(T newEntry) {
lastIndex++;
if (lastIndex >= heap.length) {// 数组heap已满
// 将数组长度加倍
}
int newIndex = lastIndex; // 下一个空闲的数组位置的索引
int parentIndex = newIndex / 2; // 空闲位置的双亲的索引
while ((newIndex > 1) && newEntry.compareTo(heap[parentIndex]) > 0) {
heap[newIndex] = heap[parentIndex]; // 将双亲移动到空闲位置
newIndex = parentIndex; //更新索引
parentIndex = newIndex / 2;
}
heap[newIndex] = newEntry; // 将新元素放到正确位置
}4. 堆:删除根 将半堆转化为堆 为了删除堆的根,首先用堆的最后一个子结点替换根,这一步骤形成一个半堆,因此要使用方法reheap将半堆转换为堆。
删除根算法 public T removeMax() {
T root = null;
if (!isEmpty()) {
root = heap[1]; // 返回值
heap[1] = heap[lastIndex]; // 形成半堆
lastIndex--; // 堆的大小减1
reheap(1); // 转化为堆
}
return root;
}
private void reheap(int rootIndex) {
boolean done = false;
T orphan = heap[rootIndex];
int largerChildIndex = 2 * rootIndex;
while (!done && (largerChildIndex <= lastIndex)) {
int leftChildIndex = largerChildIndex; // 等于根的子节点中较大者的索引
int rightChildIndex = leftChildIndex + 1;
if ((rightChildIndex <= lastIndex)
&& heap[rightChildIndex].compareTo(heap[largerChildIndex]) > 0)
largerChildIndex = rightChildIndex;
if (orphan.compareTo(heap[largerChildIndex]) > 0) {
heap[rootIndex] = heap[largerChildIndex];
rootIndex = largerChildIndex;
largerChildIndex = 2 * rootIndex;
} else
done = true;
}
heap[rootIndex] = orphan;
}5. 堆:创建堆 使用add 从一组对象创建堆,可以使用add方法将每个对象插入到初始为空的堆中。这种方式创建堆是O(nlogn) 使用reheap 创建堆更高效的方式是使用reheap方法。先将堆的元素从索引1开始放进数组中,这个数组可以表示为一个完全二叉树,这棵二叉树含有可转化为堆的半堆,叶子结点是半堆,额也是堆。 使用reheap将一个数组的元素转化为堆,这种方式创建堆是O(n) 6. 堆:堆排序 使用堆可以对数组排序。如果将数组元素放在一个最大堆中,将得到降序排序的元素。使用reheap而不是add,是从一个数组的元素创建堆的更高效方式。 转载请并标注: “本文转载自 linkedkeeper.com ” ©著作权归作者所有 |