Proxy / Delegate 设计模式
|
您目前处于:Architecture
2015-08-20
|
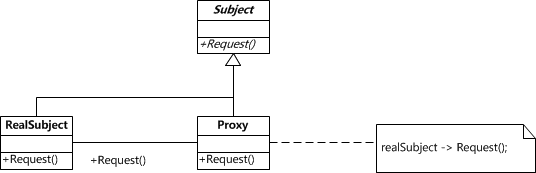
系列文章:定义 为其他对象提供一种代理以控制对这个对象的访问 结构
示例 Subject 定义了 RealSubject 和 Proxy 的公共接口,这样就可以在任何使用 RealSubject 的地方使用 Proxy。 abstract class Subject {
public abstract void Request();
}RealSubject 定义了 Proxy 所代表的真实实体。 class RealSubject extends Subject {
@Override
public void Request() {
System.out.println("真实的请求");
}
}Proxy 保存一个引用使得代理可以访问实体,并提供一个与 Subject 的接口相同的接口,这样代理就可以用来替代实体。 class Proxy extends Subject {
private RealSubject real;
@Override
public void Request() {
if (null == real) {
real = new RealSubject();
}
real.Request();
}
}样例 定义逻辑层接口协议: @protocol LogicInterface<NSObject> - (void)applicationLaunching; // 启动应用 @end 声明 Logic 类,即代理的人: @interface Logic : NSObject<LogicInterface> // 实现协议 + (id<LogicInterface>)getInstance; @end Logic 实现文件: static Logic *gStaticLogic = nil;
@interface Logic()<LogicInterface> // 实现协议
@property (nonatomic, strong)TcpModule *tcpModule;
@end
@implementation Logic
+ (Logic *)getInstance {
@synchronized(self) {
if (gStaticLogic == nil) {
gStaticLogic = [[Logic alloc]init];
}
return gStaticLogic;
}
}
- (void)applicationLaunching {
// tcpModule 是真实的具体处理 module
[self.tcpModule applicationLaunching];
}
@end声明一个 ViewController 视图层: @interface HomeViewController : UIViewController @end ViewController 实现文件: @implementation HomeViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[[Logic getInstance]applicationLaunching];
}
@end
转载请并标注: “本文转载自 linkedkeeper.com ” ©著作权归作者所有 |